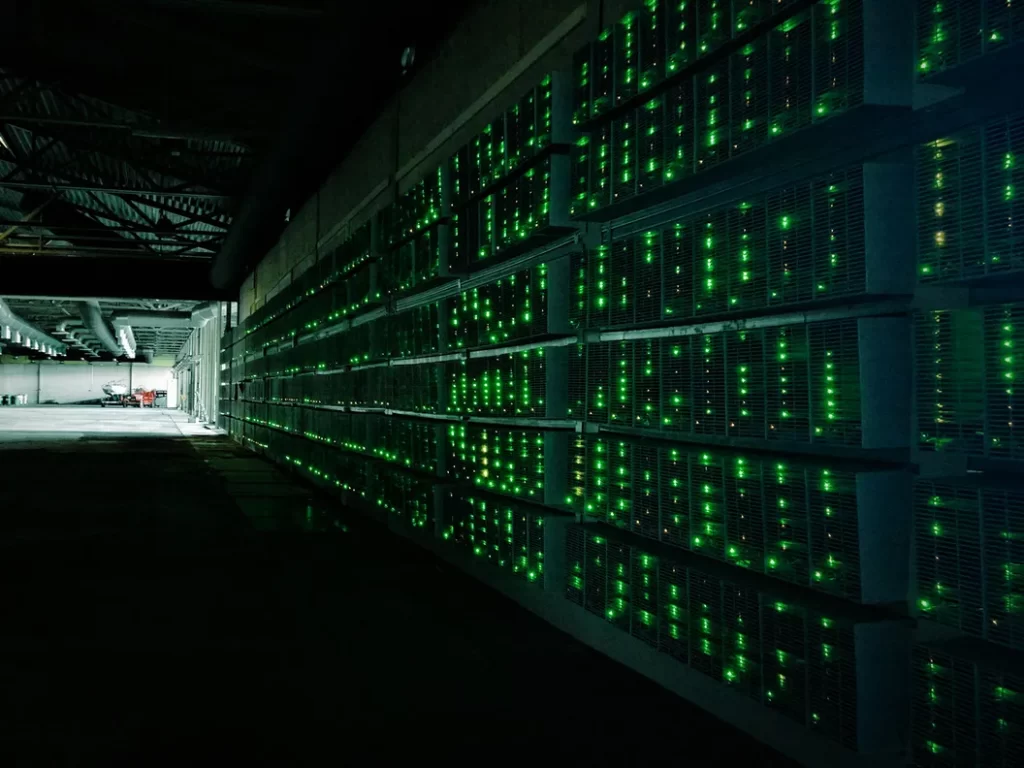

Crypto Miners Are Still Building

Throughout the summer, CoinDesk traveled to two U.S. states to visit bitcoin (BTC) mines to see how, even in the midst of a crypto winter, miners are still building data centers to power the Bitcoin network.
Firstly, Bitcoin miners have had a tough few months as the price of the world’s largest cryptocurrency has dropped precipitously.
With low bitcoin prices, miners’ revenues have diminished, and some have been forced to sell their mined tokens, machines and even facilities for cash to run their operations.
On top of that, the Biden administration on Sept. 8 dropped a report calling for industry standards to limit cryptocurrencies’ environmental footprint. Should these fail, authorities and legislators in the U.S. should consider measures to limit or eliminate energy-intensive proof-of-work algorithms that bitcoin miners use to drive the Bitcoin network, the report recommended.
Still, bitcoin miners are busy building out more capacity. Visiting these sites shows how the industry in the U.S. is continuously iterating. Mining data centers come in many shapes and sizes, depending on the location and available energy supply.
These buildouts have borne fruit for the network, with computing power steadily growing over the past few months.
Merkle Standard and Bitmain facility in Washington
Near Washington state’s border with Idaho lies a 30-year-old paper mill that has been closed since 2020. It’s just about the last place where you’d expect to find a bitcoin mine testing some of the world’s most innovative mining rigs, but there it is.
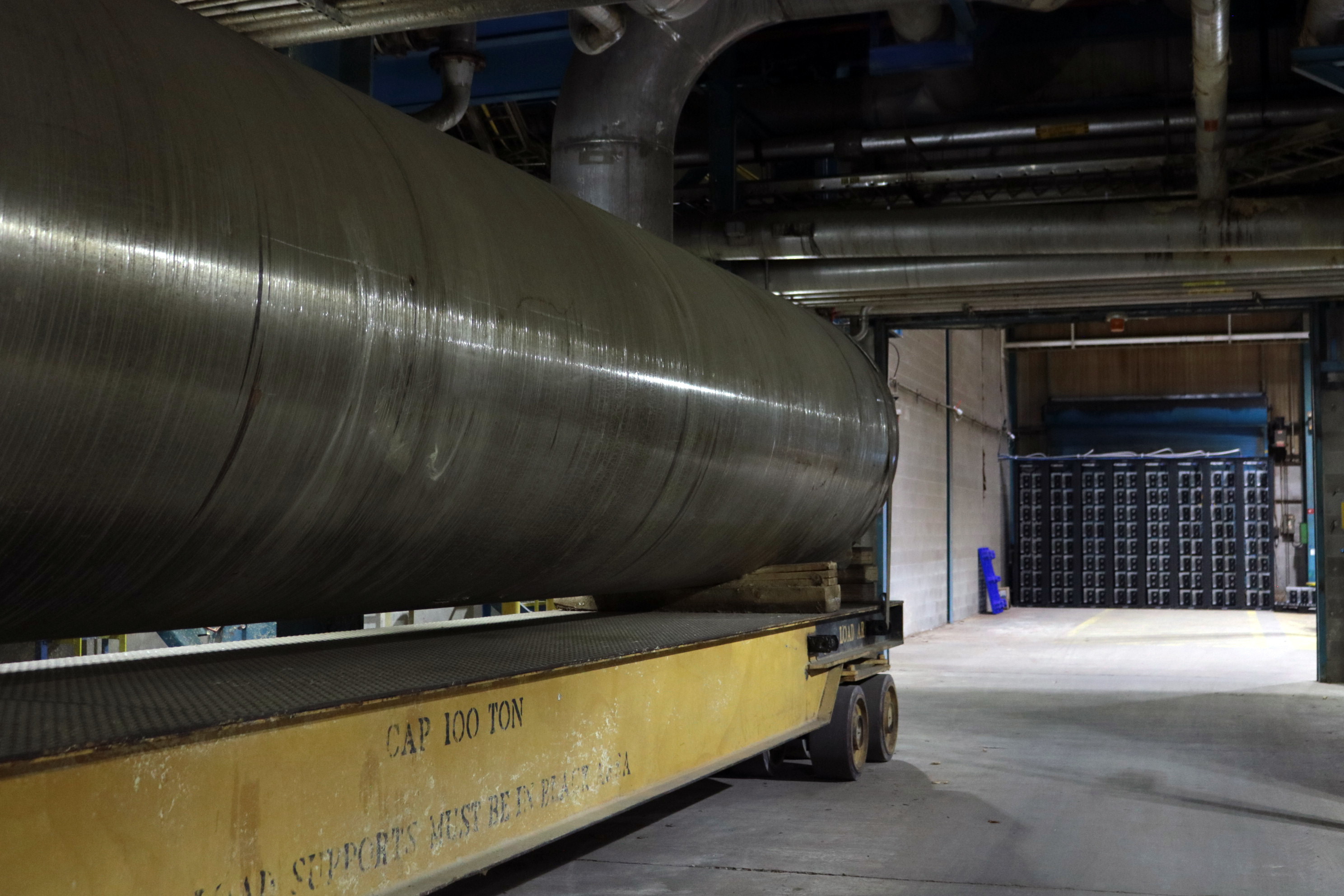

Mining rigs are running next to a 100-ton paper roller at Merkle Standard’s site in Washington state, U.S. (Eliza Gkritsi/CoinDesk)
Secondly, The facility is a co-venture between private bitcoin miner Merkle Standard and Bitmain, the world’s largest manufacturer of bitcoin mining rigs.
The site is currently capped at operating at 100 megawatts (MW),
about the annual capacity of 10 homes in the U.S., and has the electrical infrastructure to reach 225 MW, Merkle Standard Chief Operating Officer Monty Stahl told CoinDesk during a site visit.
The water treatment facility is no miscellaneous accessory. The site is a testing ground for Bitmain’s S19 XP Hydro, a mining machine that cools itself using water pipes that run near the processor chips.
In order to run these machines, “you need to understand and respect water chemistry,” Stahl said. Operating these pricey rigs with the right type of water is key to their longevity and efficiency, he added.
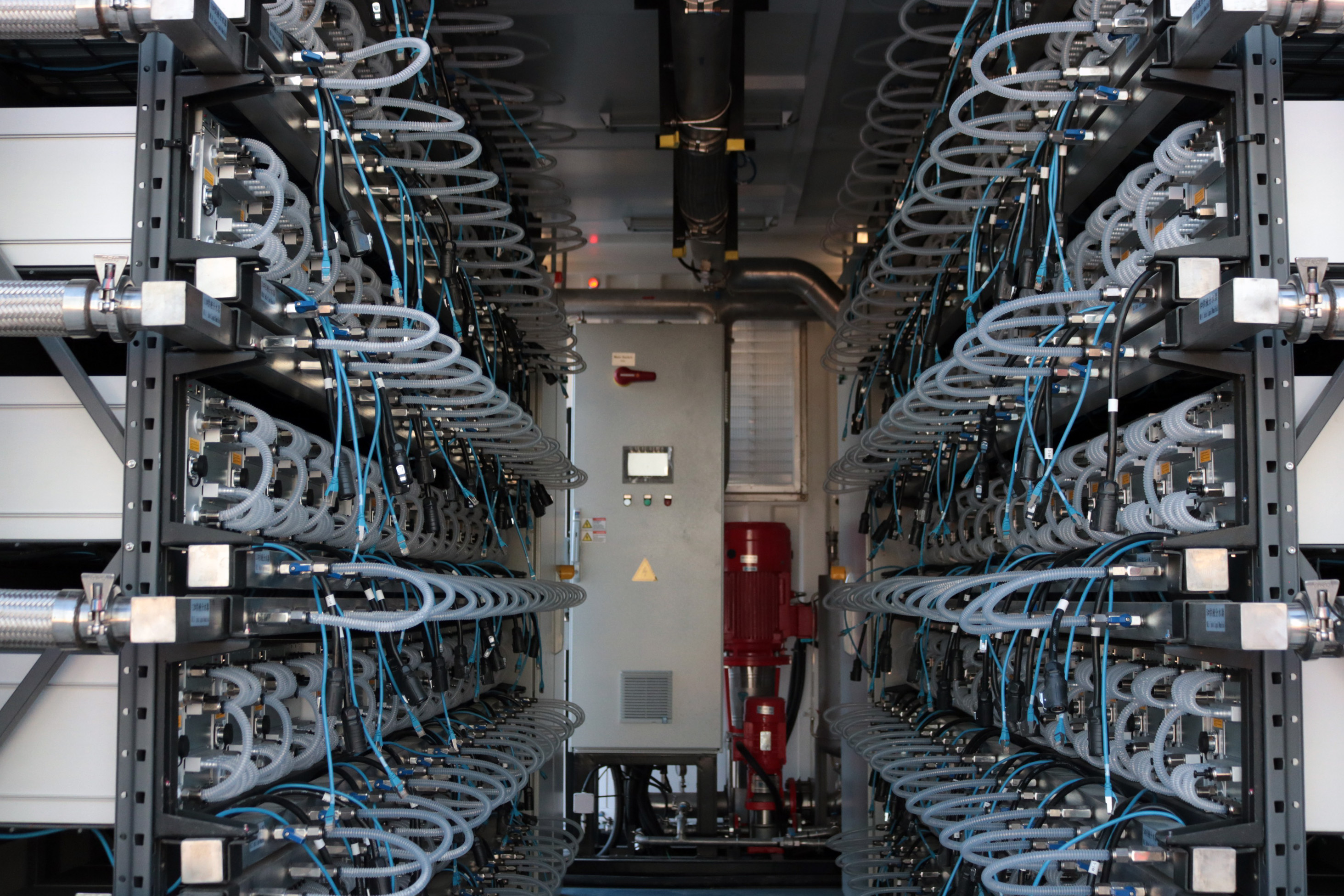

Bitmain Antminer S19 Hydro mining rigs, the company’s latest technology, installed at a Merkle Standard facility in Washington state. (Eliza Gkritsi/CoinDesk)
“In my opinion, this is superior technology and more scalable than immersion,”
The site manager also takes pride in the blue collar talent that he inherited from the mill.
Most of the mining, however, takes place outside of the paper mill, in Bitmain’s Antbox mining containers. Merkle Standard has preserved the paper mill and plans to reopen it.
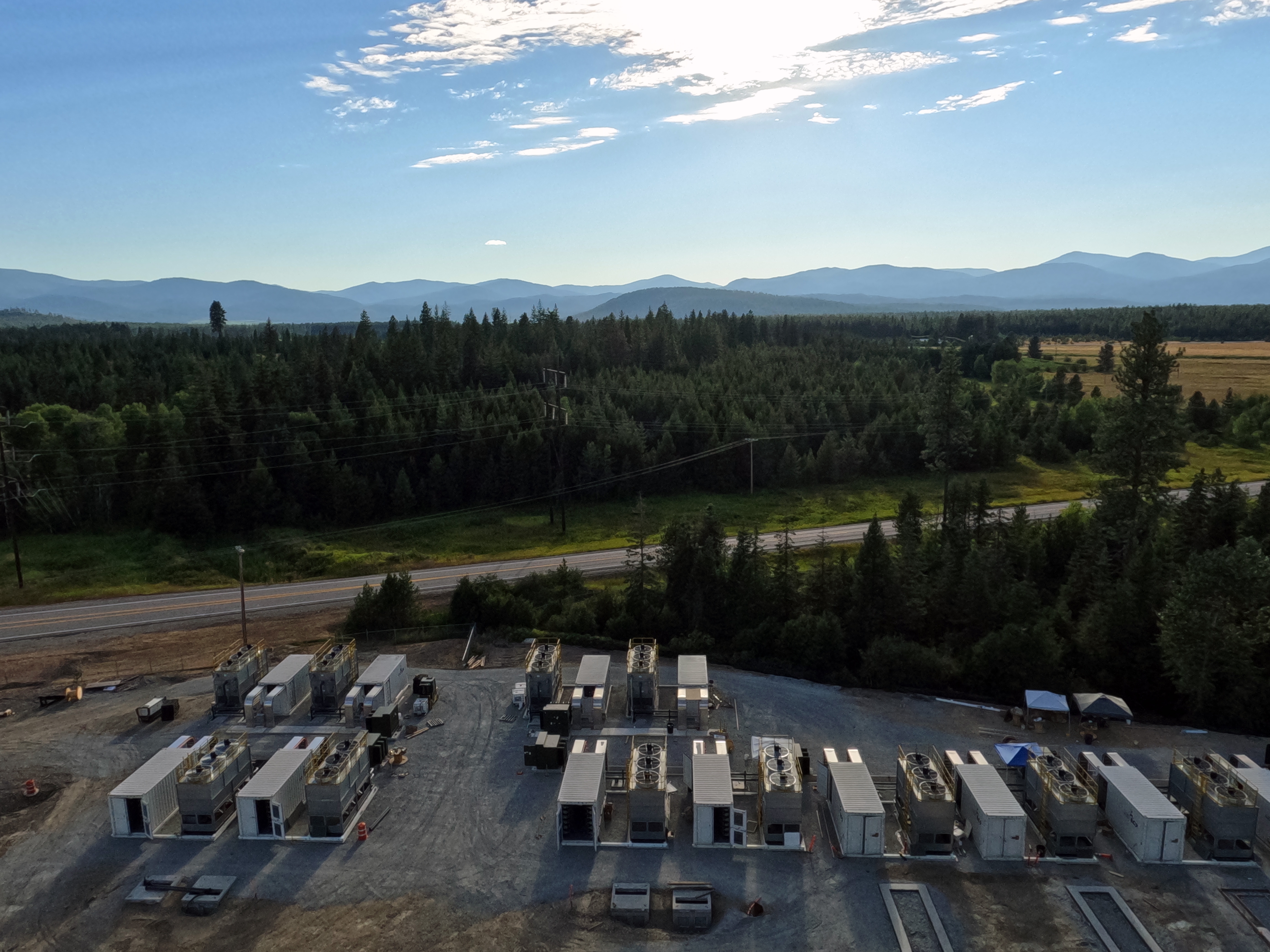

Bitmain Antbox containers sit at Merkle Standard’s bitcoin mine in Washington state. (Eliza Gkritsi/CoinDesk)
Thirdly, Walking through the cavernous halls of the paper mill, steps echoing, feels like something out of a horror movie.
Time stopped when the paper mill closed due to bankruptcy in 2020, but it never started again.
A few details in the space are stark reminders of the people who are no longer there: a microscope standing upright at the lab ready to be used, a plaque commemorating the one-millionth ton of newsprint produced in 1994, a board noting the longest-serving employees.

A board notes employees’ long service at a closed paper mill that is now a crypto mine. (Eliza Gkritsi/CoinDesk)
CleanSpark, Atlanta Area, Georgia
CleanSpark (CLSK) was founded in the late 1980s as a software company, only to meander from one business to another; Its evolution as a bitcoin miner is apparent across two sites in Georgia.
At College Park, near Atlanta’s Hartsfield airport – the world’s biggest by passenger traffic – is a 47 MW bitcoin mine divided into four parts.
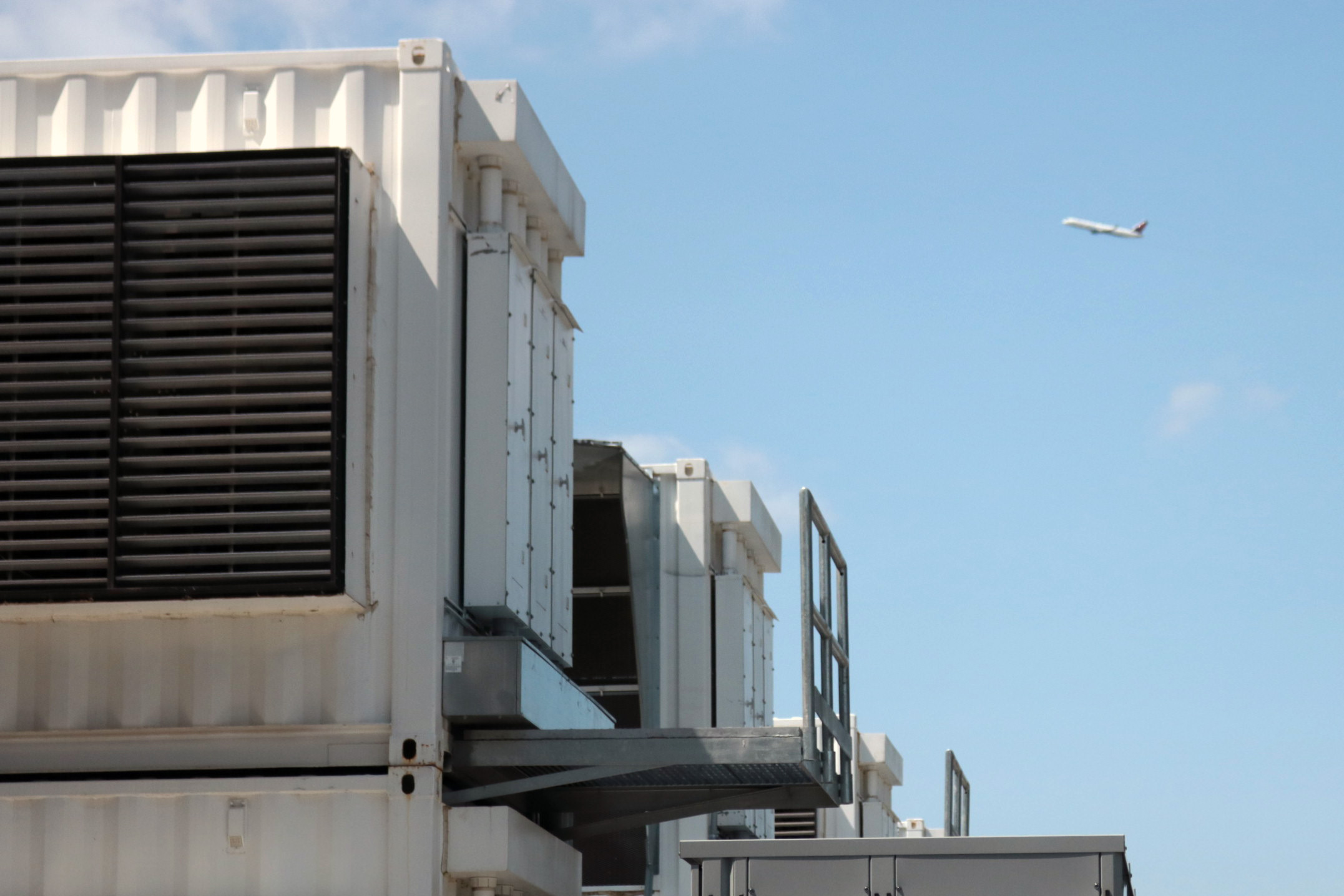

A plane taking off from Atlanta’s Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport near CleanSpark’s bitcoin mining facility in College Park, Georgia. (Eliza Gkritsi/CoinDesk)
The site was originally a traditional data center with about 50 clients, which have slowly been leaving the building. The building uses what looks like air-conditioning equipment to cool down the machines;
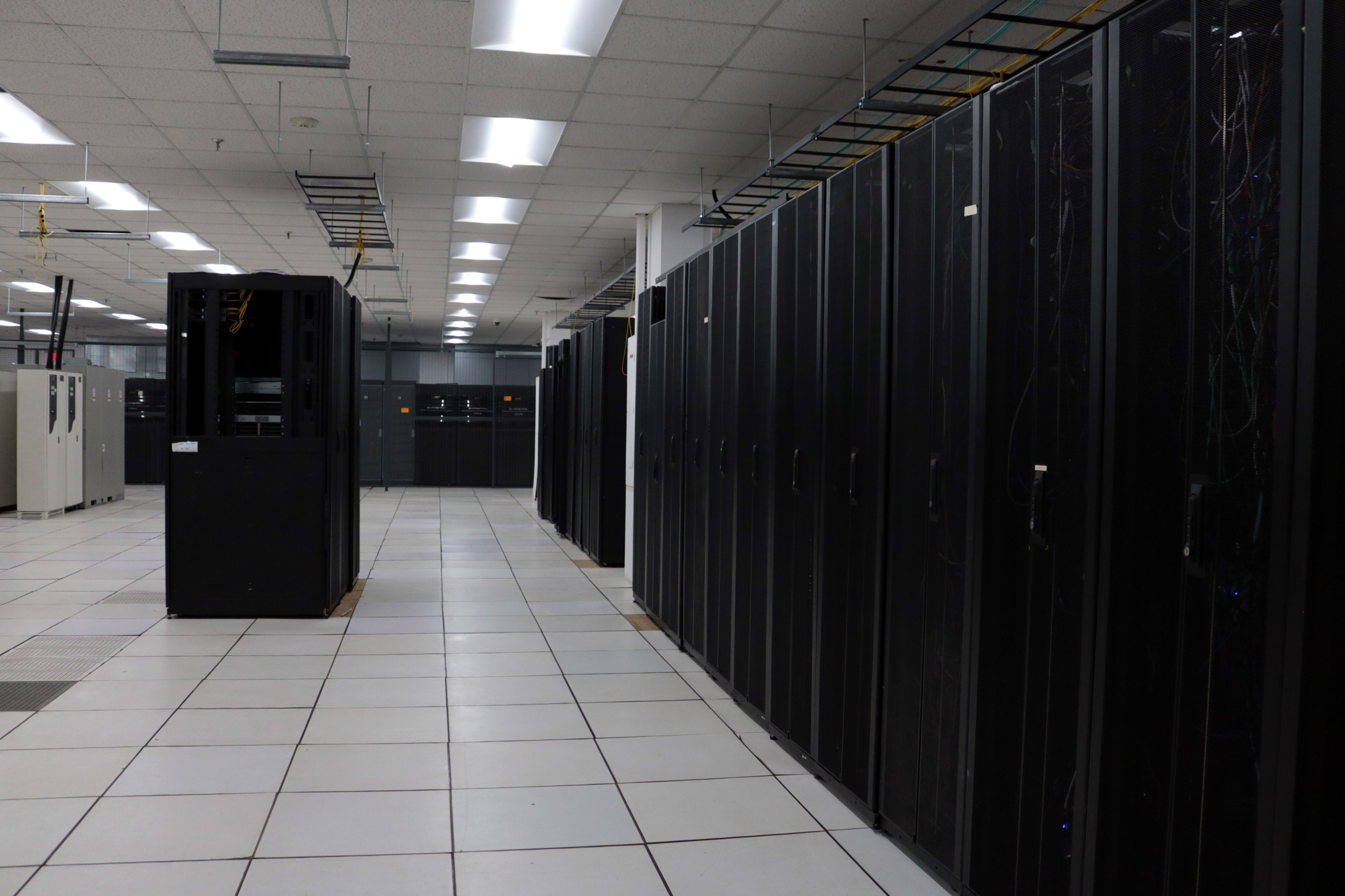

The original data center racks at CleanSpark’s facility in College Park, Georgia. (Eliza Gkritsi/CoinDesk)
Just next door is another bitcoin mine that uses evaporation cooling.
One of the walls of this building is a kind of perforated wet wall the air goes through before coming into the building.
On another wall are fans to pull the air into the room.
When water evaporates from a surface, the surface’s temperature drops, much like when sweating during a run.
The company says it plans on eventually retiring this system for another type of evaporative cooling.
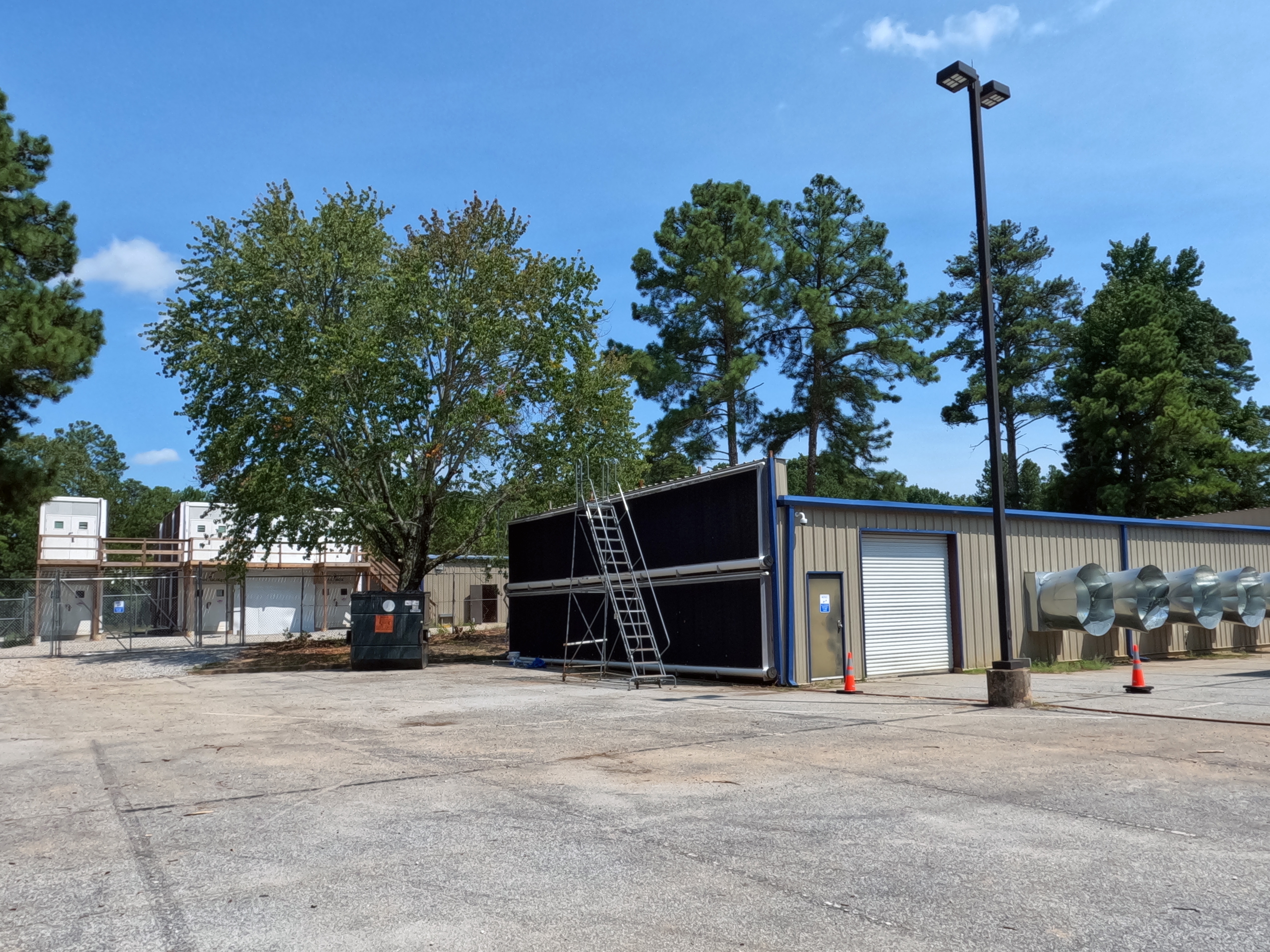

CleanSpark’s two evaporation cooling facilities in College Park, Georgia. (Eliza Gkritsi/CoinDesk)
A few mining containers made by Bitmain and called AntBoxes sit outside the building, which work similarly to the evaporation cooling building; their back walls are fitted with streaks of a cardboard-like material where the steam comes through.
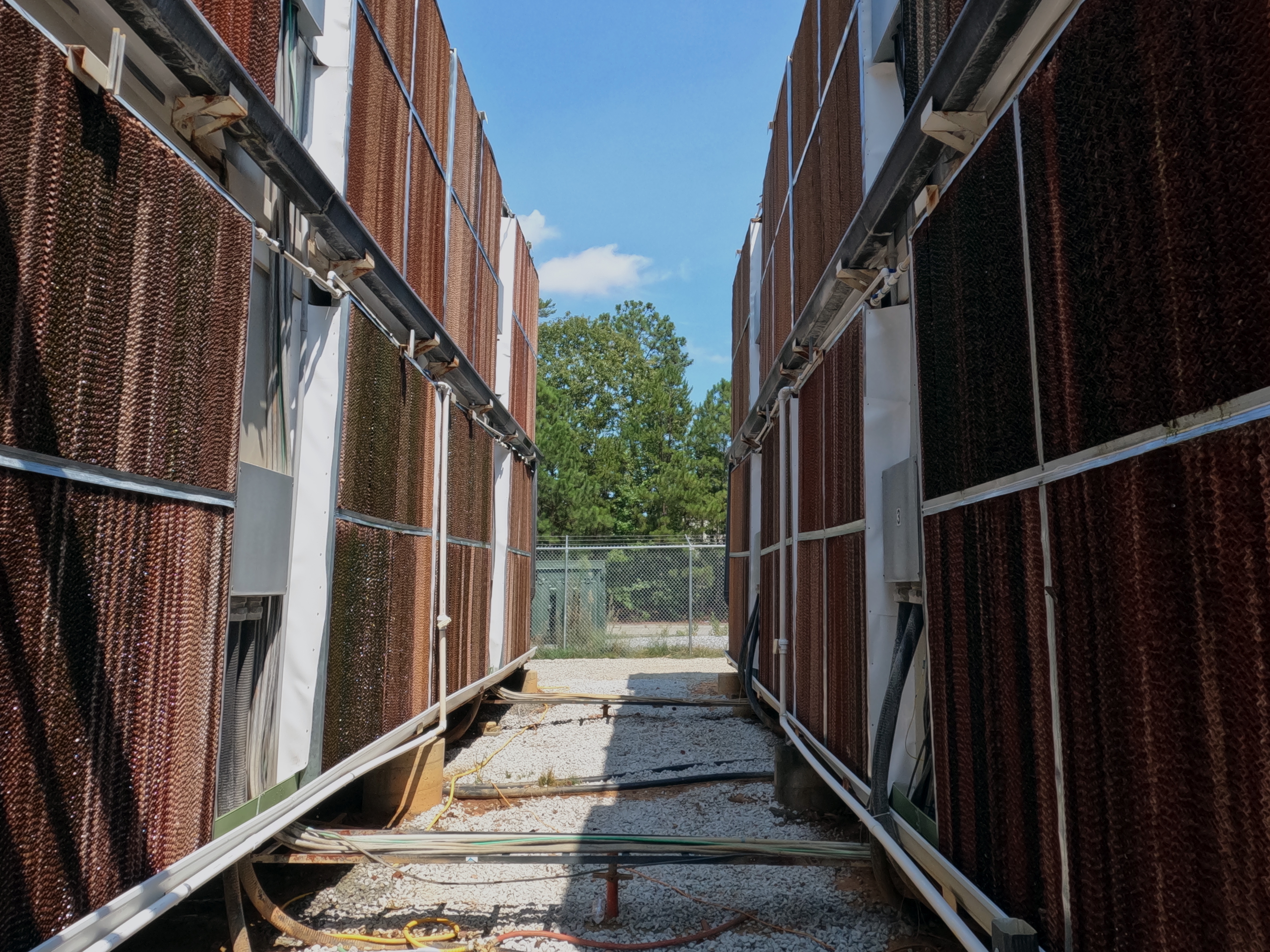

The backs of evaporation-cooled Bitmain Antboxes in CleanSpark’s College Park facility. (Eliza Gkritsi/CoinDesk)
The final part of the College Park facility of which the CleanSpark team is proudest is a set of air-cooled containers running outside a building the company has designed, laid up in two stories. This is the loudest part of the facility, which is why the company built a sound-diminishing wall and planted trees around this building.
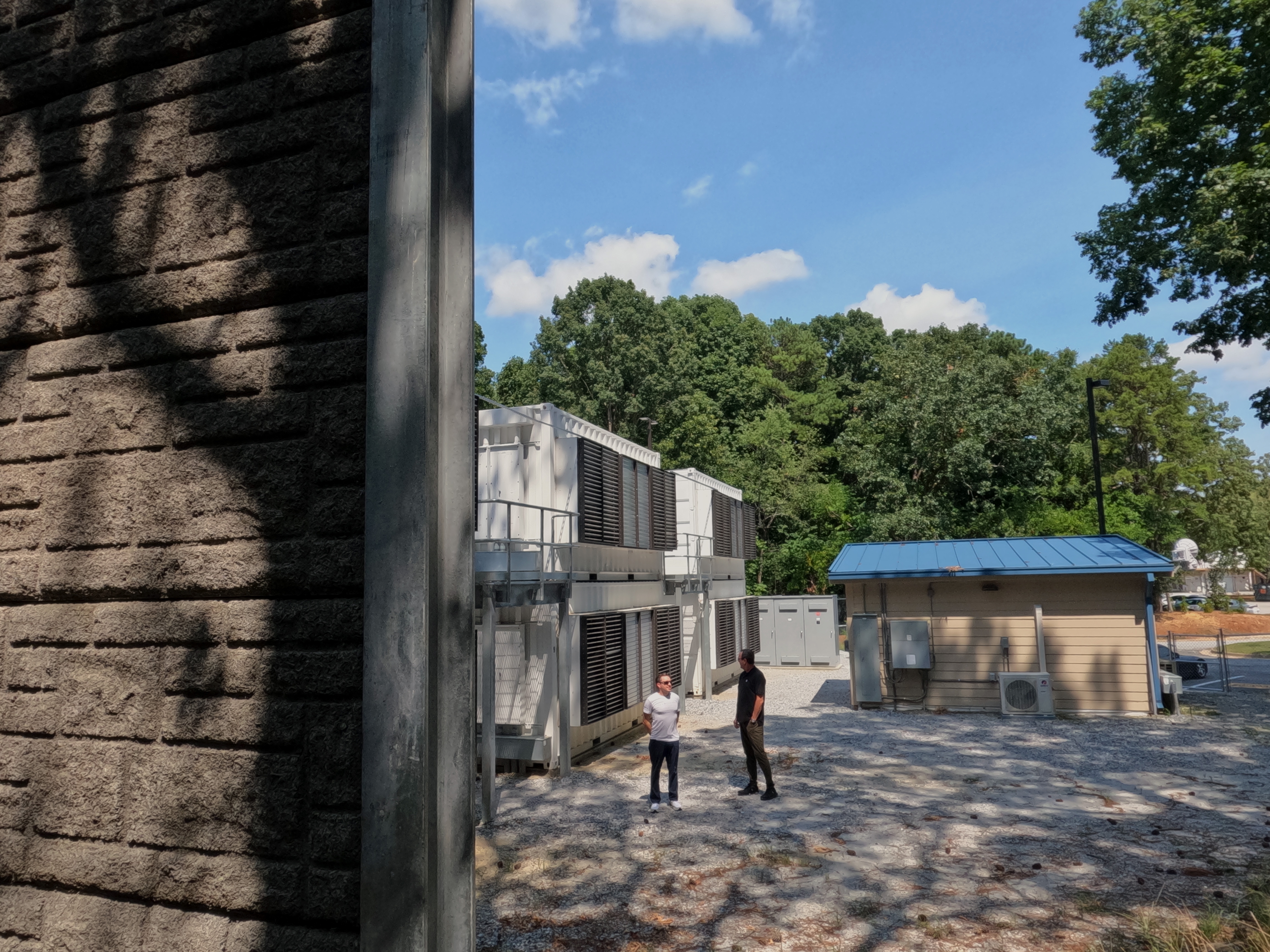

CleanSpark CEO Zach Bradford and Executive Chairman Matt Schultz chat next to the company’s CleanBlock site in Georgia, behind a soundproofing wall. (Eliza Gkritsi/CoinDesk)
The temperature changes every few seconds as one walks through what the company calls “Clean Block.” Hot air comes out of one side of the containers and cool air comes into the other. It’s like walking through a supermarket with an open freezer door in one aisle and a hot lamp heating food immediately in the next.

Immersion cooling sounds more like a spa, said CleanSpark’s Schultz. (Eliza Gkritsi/CoinDesk)

CleanSpark’s immersion-cooled bitcoin miners at a site in Norcross, Georgia. (Eliza Gkritsi/CoinDesk)
About 40 minutes away, in Norcross, is CleanSpark’s newer facility.
Instead of loud fans, “it’s like being in a spa,” remarked Matthew Schultz. He wasn’t wrong. The sound of the mineral oil flowing does sound like a relatively quiet indoor fountain.
Bitfarms, Moses Lake, Washington
“That’s an old semiconductor plant,” said Jayden Perry excitedly.
The manager of the Bitfarms (BITF) sites in Moses Lake, Washington,
was pointing to what looked like a steel and concrete giant sleeping in a golden wheat field,
right by one of the Bitfarms facilities.
The friendly regional manager admitted that he likes learning about now-abandoned industrial facilities in Washington’s agricultural heartland.
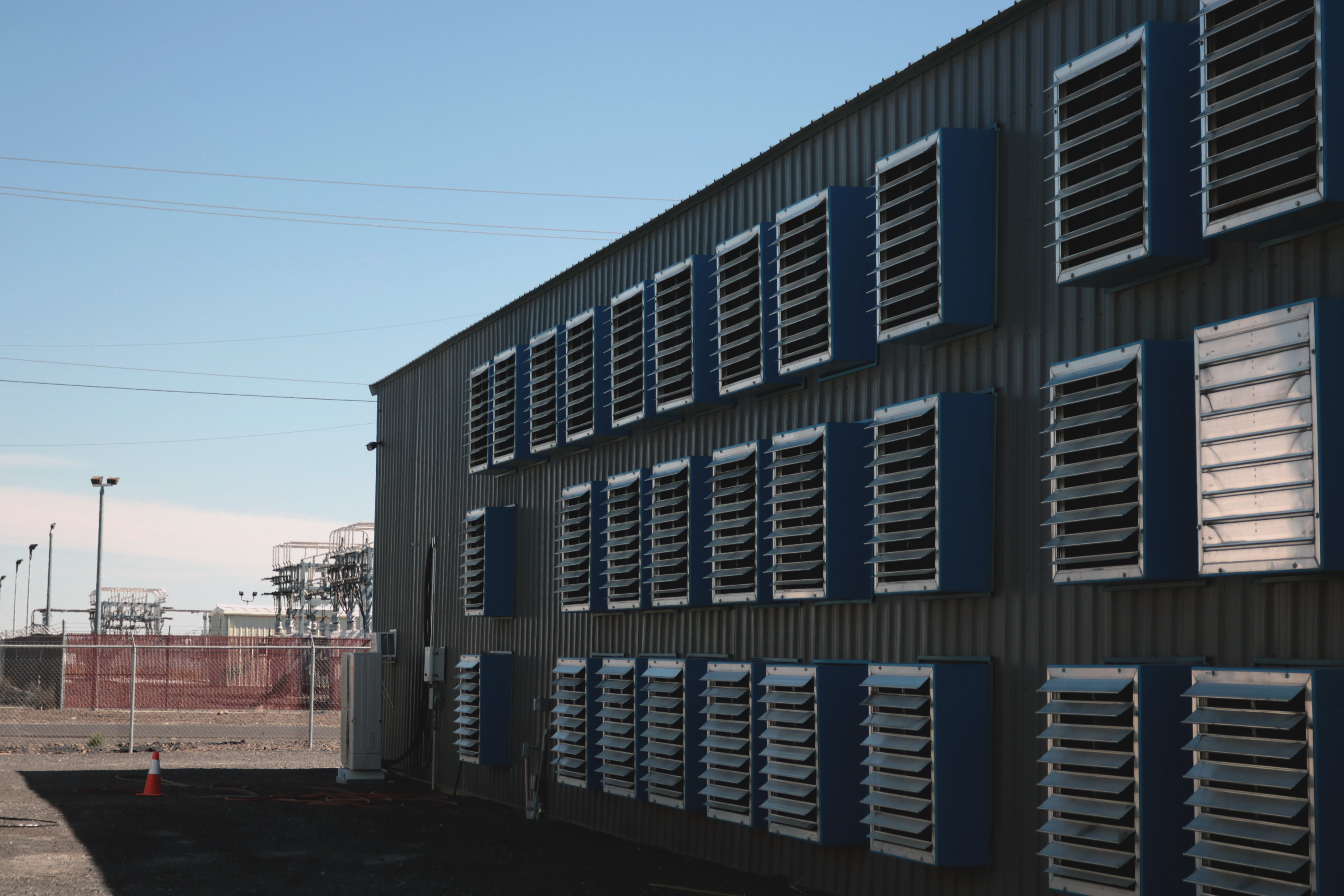

The Bitfarms mining facility in Washington is right next to an electricity substation that transforms high-voltage power to low-voltage so that it can be used by industries and businesses. (Eliza Gkritsi/CoinDesk)
The Canadian mining company bought two sites in November 2021 from an undisclosed party and is working to revamp them to Bitfarms’ standards.
The sites are all air-cooled, meaning they use the outside air and sets of fans to keep the temperature low,
as temperatures most of the year are cool in this part of the country. Another is to install Antminer S19J Pro miners.

Fans help the flow of air so that Bitfarms mining rigs can stay cool. (Eliza Gkritsi/CoinDesk)
The two sites, which total 20 MW and around 6,100 machines,
run on hydropower supplied by the Grand Coulee dam,
the biggest in the U.S. by power produced crypto.

Part of the revamp of the bitcoin mine that Bitfarms bought in Washington includes re-organizing the wires. (Eliza Gkritsi/CoinDesk)
The Bitfarms facilities aren’t the most exciting or innovative of the bunch,
but they are nonetheless part of the network of computers that keeps bitcoin going.
The sites are also indicative of a trend that has just started amid the crypto winter: consolidation. The mining firm is also expanding across four countries – crypto the other three being Canada, Paraguay, and Argentina – in order to shield itself from geographic risks.
The bitcoin mines on our latest trip show something that is often forgotten:
While supporting a decentralized crypto infrastructure revolutionizing finance,
these facilities are just huge, noisy data centers that consume a lot of power.
Miners are essentially working on data center design,
and the technology going into these facilities, like cooling,
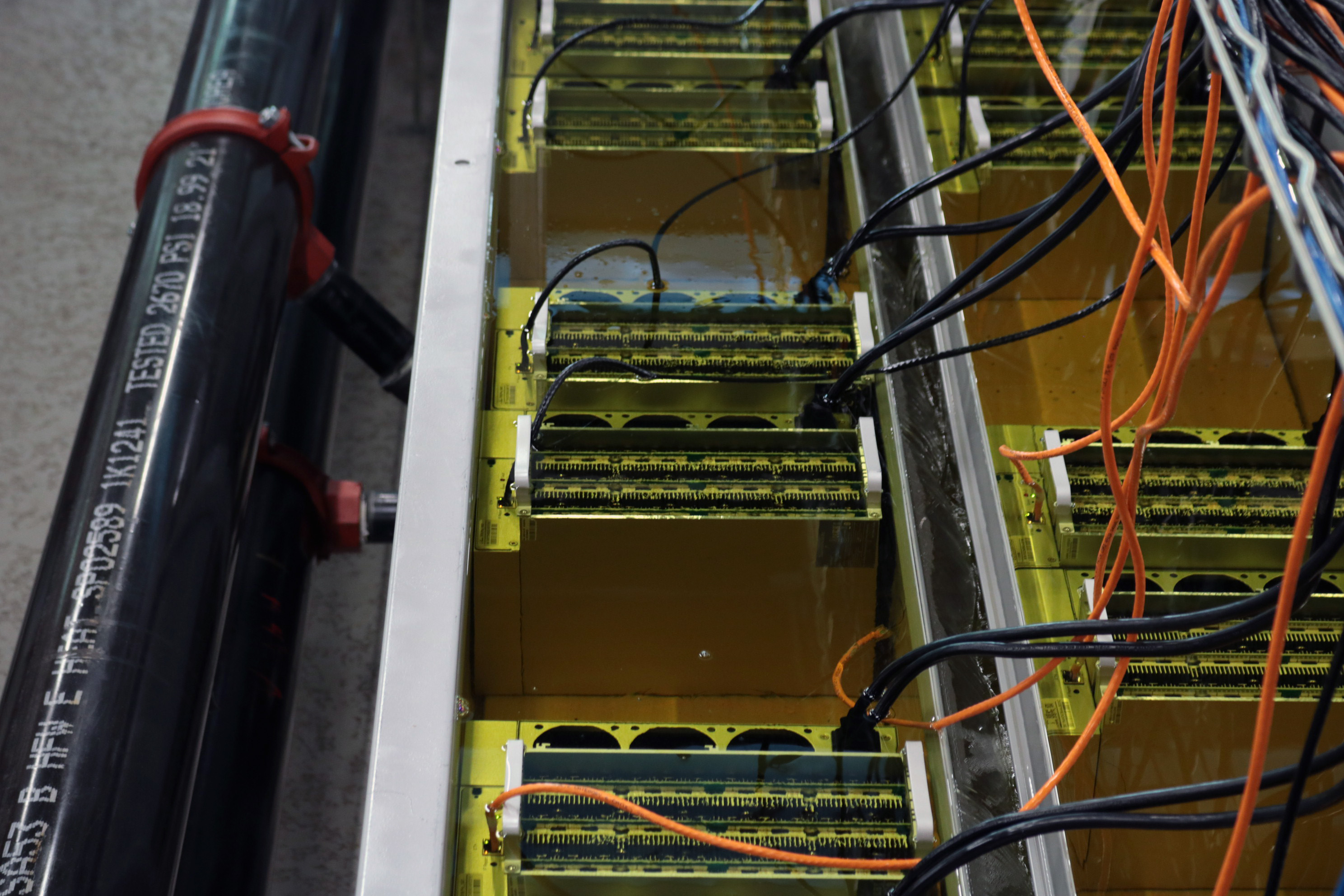

CleanSpark is experimenting with how many bitcoin mining machines it can put in a single immersion-cooled tank while overclocking them, meaning running them more intensely than the manufacturer’s suggestion. (Eliza Gkritsi/CoinDesk)
As much as the Bitcoin crypto network is in many senses designed to consume a lot of energy,
mining firms have a built-in incentive to keep their costs low –
or risk falling behind a very competitive market.
This pushes them to try out different ways to build and operate data centers;
from mining at the edges of the world, like Siberia,
to plunging millions of dollars of equipment into mineral oil to keep them cool.
Some miners, like Hive Blockchain and Hut 8,
are already trying to diversify into other data centers like those processing artificial intelligence and cloud computing.
Perhaps in just a few years,
In Conclusion, your Google Maps directions or
your Yelp reviews could be processed in a data center that was inspired by bitcoin mines crypto.





Responses